Step-growth polymerization
The reaction between hydroxyl and carboxyl groups to generate an ester bond also gives a bi-product of water. That is why it is called a condensation reaction and it is also an equilibrium reaction that may run backwards, i.e. hydrolysis. In order to give high conversion and the water has to be removed.
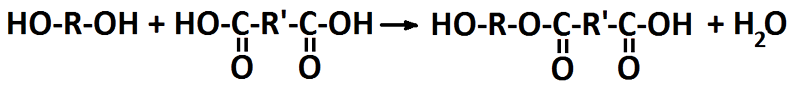
Ester synthesis from a diol and a diacid where R and R’ denotes unspecified organic compounds.
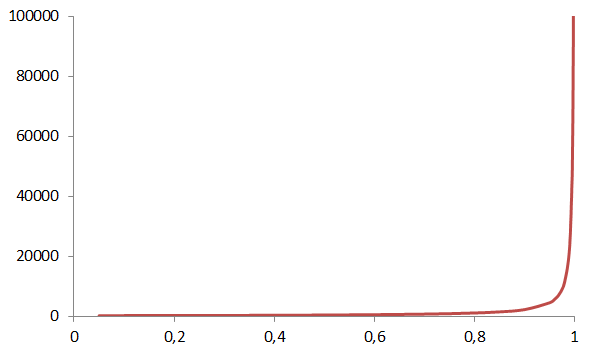
The relation between conversion, p, and degree of polymerization, is described by the Carother’s equation:
The degree of polymerization is the ratio of to the molar mass of the repeating unit , and p is the consumption of either reactive group, e.g. the hydroxyl groups in the example above. Equation 3 tells that it will take 99 % conversion to reach a degree of polymerization of 100. This is equivalent to a of 12 200 g/mol for PA66 shown in Figure 5, which is a reasonable molar mass for that particular polymer.
Task
Make a graph as function of conversion for the PA66 example.
It is also essential that the molar ratio, r, between the two reactants, for the current example r = [OH]/[COOH], is kept very close to one throughout the whole polymerization process. The Carother’s equation can be modified to cover also non-unity r values as:
It may both be difficult to measure very accurately and to find chemicals that are sufficiently pure. Common analytical grades are in general 98.5% pure. The composition of the 1.5% residue is very important to the outcome. Presence of mono-functional compounds will stop propagation.
There are a number of ways to manage the difficulties of maintaining equimolar ratio in order to reach high molar mass. Interfacial polymerization, salt dehydration, ester interchange polymerization and step polyaddition are examples of such strategies.
Make a graph as function of conversion for the PA66 example

All efforts have been made to ensure materials created by the EDU comply with current accessibility guidelines (JISC: Support for learners with disabilities).
If further assistance is required with accessibility matters please contact the student support section in your academic partner UHI: Accessing learner support.
We welcome any comments on how to improve this unit. Please feel free to pass these on at any time.
If you have any difficulty viewing this resource please contact EDU (edu@uhi.ac.uk) with:
- the name of the resource;
- a description of the problem (please give as much detail as possible);
- the section of the resource where the problem occurred;
- your internet browser (you can check your browser version at: http://detectmybrowser.com/).
UHI provides links to external sources of information and may refer to specific Web sites, products, processes or services within this resource. Such references are examples and are not endorsements and whilst every effort is taken to ensure the accuracy of information provided UHI is not responsible for any of the content or guidance. You are advised to exercise caution.
Audio
Video
Reading
Download
Information
External link
Activity
Question
Asterisk
Discussion
Collaboration
Reflection/journal/log
History
Pause for thought
Download a copy of this resource in PDF format.
You can also print individual pages by printing directly from the browser.